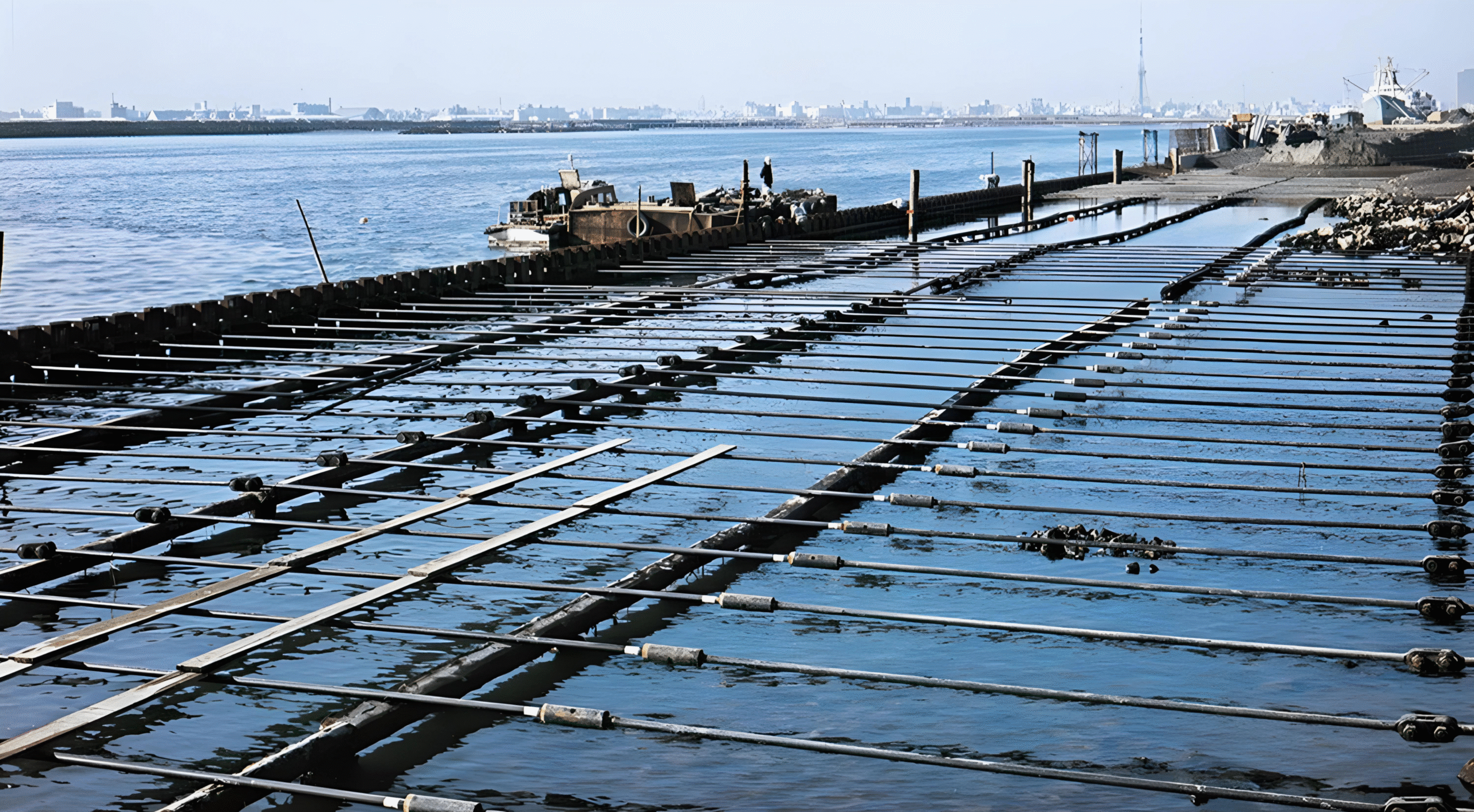
Introduction: Why Sheet Pile Walls Need Anchorage
Sheet pile retaining walls are one of the most widely used retaining structures for stabilising foundation soils along riverbanks, ports, quay walls, and urban excavations. While short walls can act as cantilevers, taller walls or those exposed to higher passive pressures and surcharge loads generally require anchorage to maintain stability and reduce excessive lateral deflection. A well-designed anchored sheet pile wall safely transfers anchor forces into stable ground, creating a permanent, cost-effective solution for challenging sites.
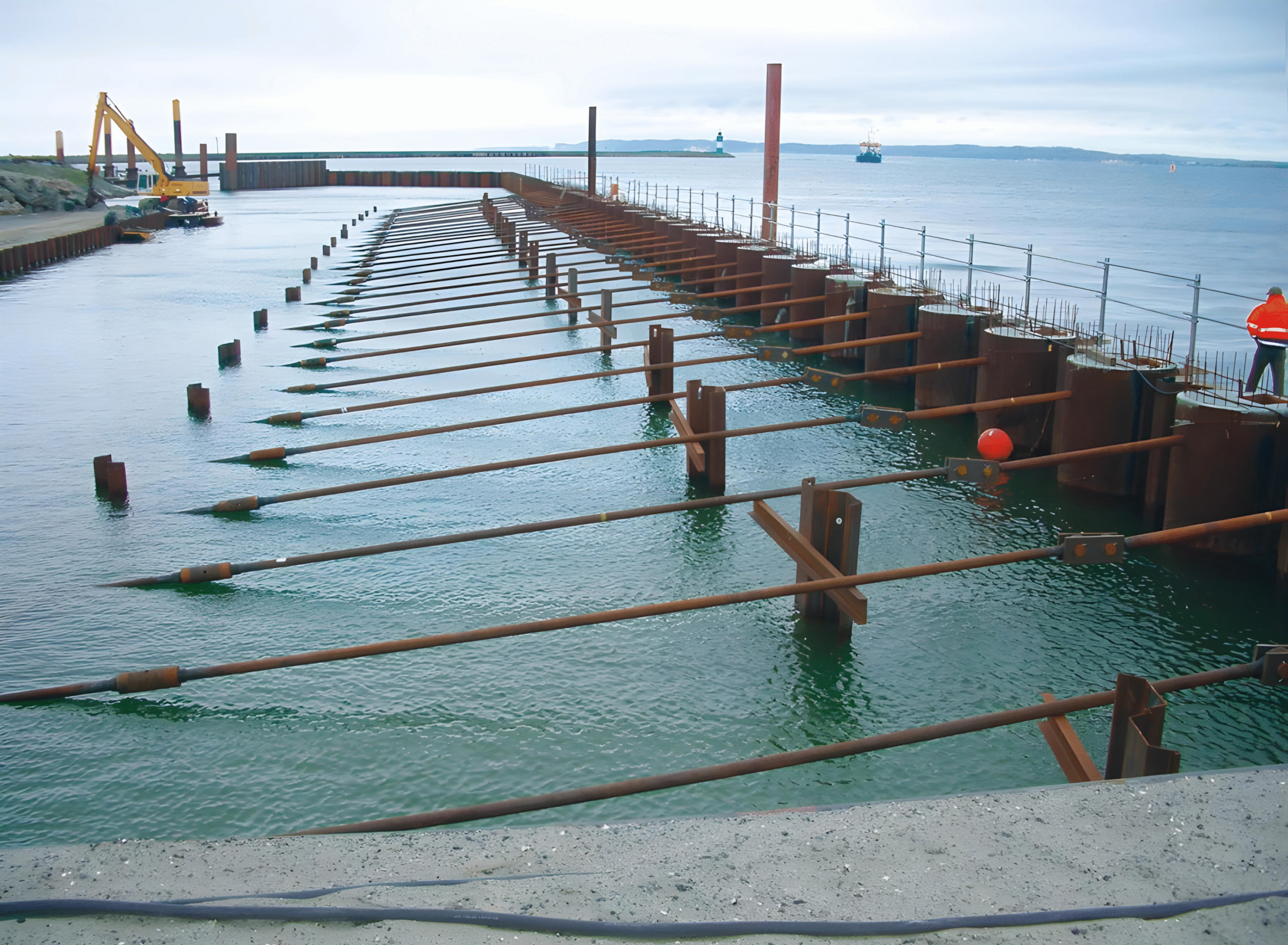
Basic Mechanics: How Anchored Sheet Pile Walls Work
The design of a sheet pile retaining wall depends on balancing active and passive earth pressures within the soil profile. The embedded depth, wall length, and soil properties — including friction angle, cohesion, and groundwater level — directly affect its capacity to resist lateral forces and maintain stability.
Gravity and Resistance: In a cantilever system, the sheet piles resist lateral loads through the embedded depth, mobilising passive earth pressure at the toe. In an anchored system, tie rods transfer part of the lateral earth pressure to an anchor block or deadman, which relies on the passive resistance of the surrounding foundation soils to resist pull-out forces.
Reduced Moments: Anchorage reduces bending moments in the piles by creating a fixed support at the tie rod connection, which lowers the required section modulus and pile thickness for the same wall height.
Role of Tie Rods in Anchored Systems
Tie rods are the tension members that carry anchor forces from the sheet pile wall to the deadman or anchor block.
Counteracting Overturning: Tie rods generate tension to counteract the horizontal active earth pressure that pushes the wall forward. This stabilises the structure, especially in layered soils with varying strength.
Spacing and Alignment: The spacing and alignment of tie rods depend on the wall geometry, element type, and site-specific loading conditions. Tie rods must maintain a straight load path to avoid unintended bending and to distribute forces evenly.

Design Examples: Single vs Double Anchored Walls
- Single Anchored Wall: A single row of tie rods is the most common for quay walls, river slopes, or medium-height basement walls. This setup balances cost and efficiency while keeping lateral deflection within defined limits.
- Double Anchored Wall: In deeper excavations or where higher water levels and surcharge loads are present, designers may specify double anchorage. The tie rods are installed at two levels to split anchor forces and maintain a stable wall profile with minimum displacement. This is especially effective for complex soil profiles with weak surface layers over stronger foundation soils.
Construction Steps: From Pile Driving to Anchoring
Successful performance relies on careful execution:
Driving the Sheet Piles:
- Piles are driven to the required embedded depth to ensure they develop enough passive resistance.
- Geometry, alignment, and wall thickness must be checked to maintain the design position.
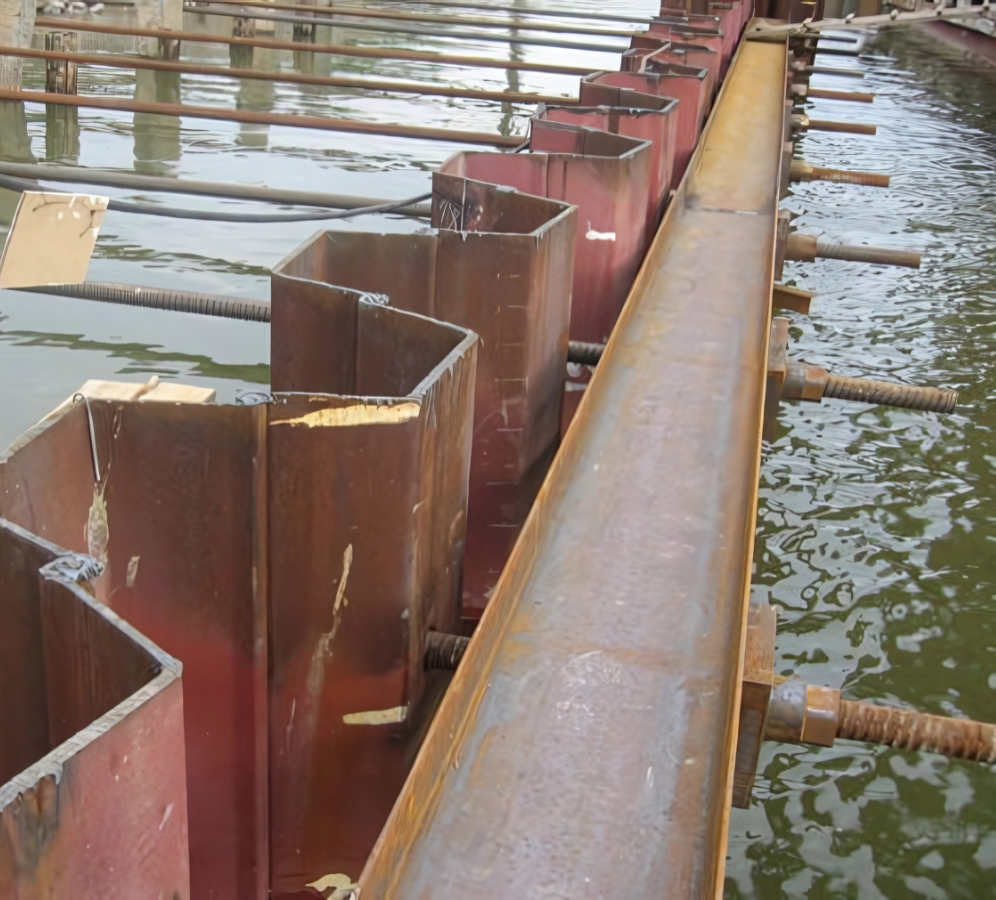
Installing Deadman or Anchor Blocks:
- Anchor blocks are buried at a defined distance behind the wall.
- The surrounding soil is compacted to achieve the necessary passive pressures.
- For sandy soils, the friction angle and compaction level are key.
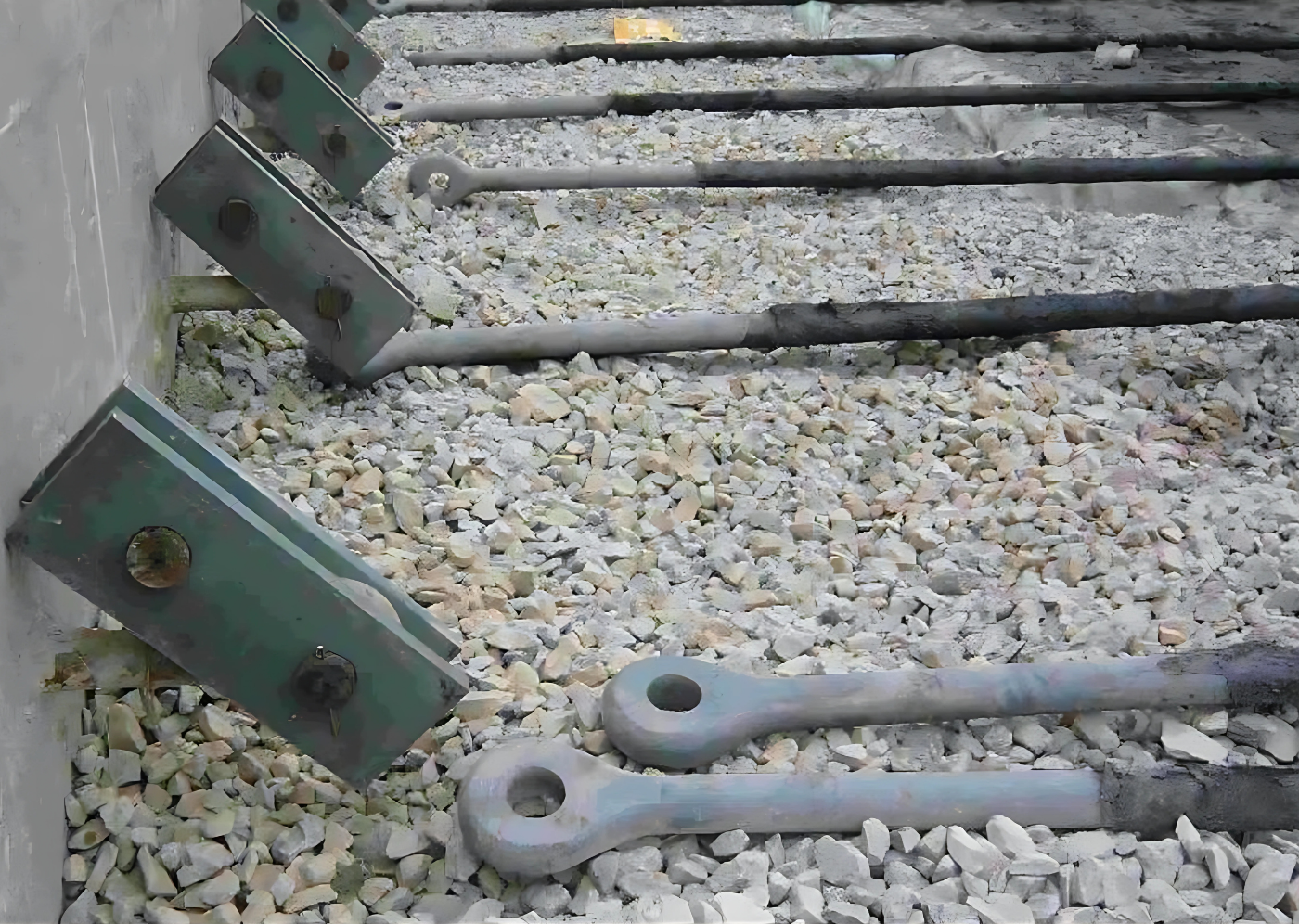
Connecting Tie Rods:
- Tie rods are inserted through wall waling beams or plates.
- Hydraulic jacks tension the rods to the calculated force.
- Hex nuts and washers fix the rods once tensioned.

Quality Control Checks
A reliable anchored sheet pile wall should always include clear QC steps:
- Alignment: Confirm that tie rods maintain a straight connection to anchor blocks. Any misalignment can lead to unwanted bending.
- Tensioning: Check that all rods are tensioned to carry the calculated anchor forces under expected loading conditions, including changes in water level or surcharge.
- Deflection Monitoring: Survey the wall face for lateral deflection. Comparing deflection against design tables helps verify that soil and groundwater assumptions match real conditions.
Durability Factors: Long-Term Performance
Anchored walls are often permanent structures exposed to harsh conditions, so protecting tie rods is essential.
- Coatings and Protection: Use hot-dip galvanising, epoxy systems, or multi-layer treatments like three-oil two-cloth for high-risk areas. In aggressive marine or brackish water, cathodic protection adds extra defence.
- Site-Specific Considerations: Soil properties, water table fluctuations, and corrosive soil layers all affect durability. Periodic inspections help maintain performance and detect early signs of deterioration.

Practical Tips: Managing Site Constraints
- Check for buried utilities, existing boundaries, or land use limitations that could affect anchor installation.
- Ensure the anchor length and embedment maintain safe distances from adjacent structures.
- For sites with poor drainage or slopes, use geotextiles and proper wall drainage to minimise water pressure build-up.
- Keep clear construction notes to record soil conditions, grouting volumes (if used), and tensioning data for future maintenance.
Conclusion
An anchored sheet pile wall is a proven, cost-effective solution for stabilising retaining structures in challenging soil profiles and water conditions. By correctly modelling soil properties, passive pressures, and anchor geometry — and by carrying out construction to the highest standards — you can ensure a robust system that controls displacement and performs reliably for decades.
If you need design assistance, practical advice, or to source high-quality tie rods and anchor systems for your next project, our team is ready to help you build with confidence.
Related Products from Aema Steel
- Steel Tie Rod Systems
- Hot Rolled U Type Sheet Piles
- Hot Rolled Z Type Sheet Piles
- Steel Pipe Piles
- Welded H Piles
Contact us today to receive a tailored offer for your upcoming project.







