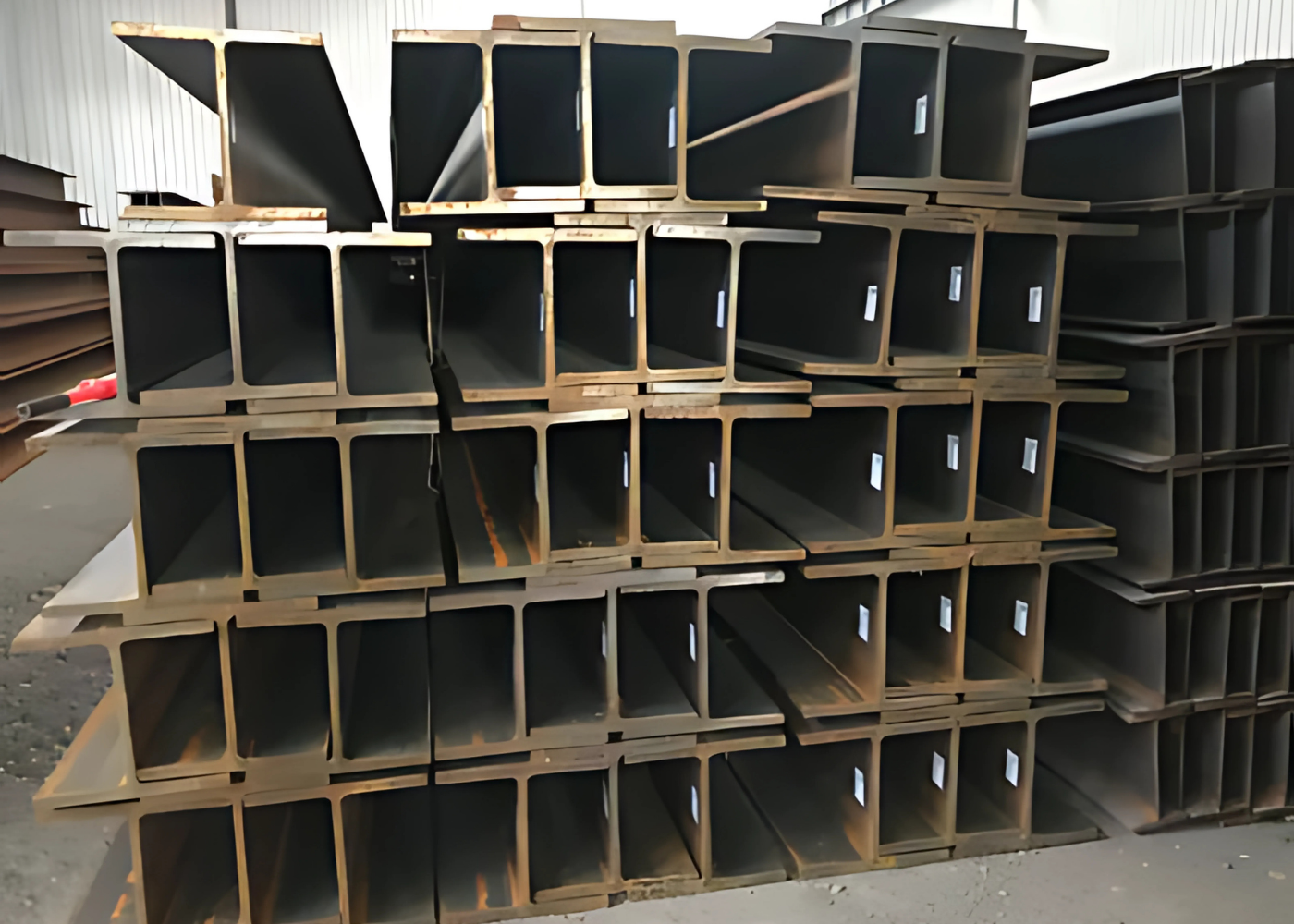
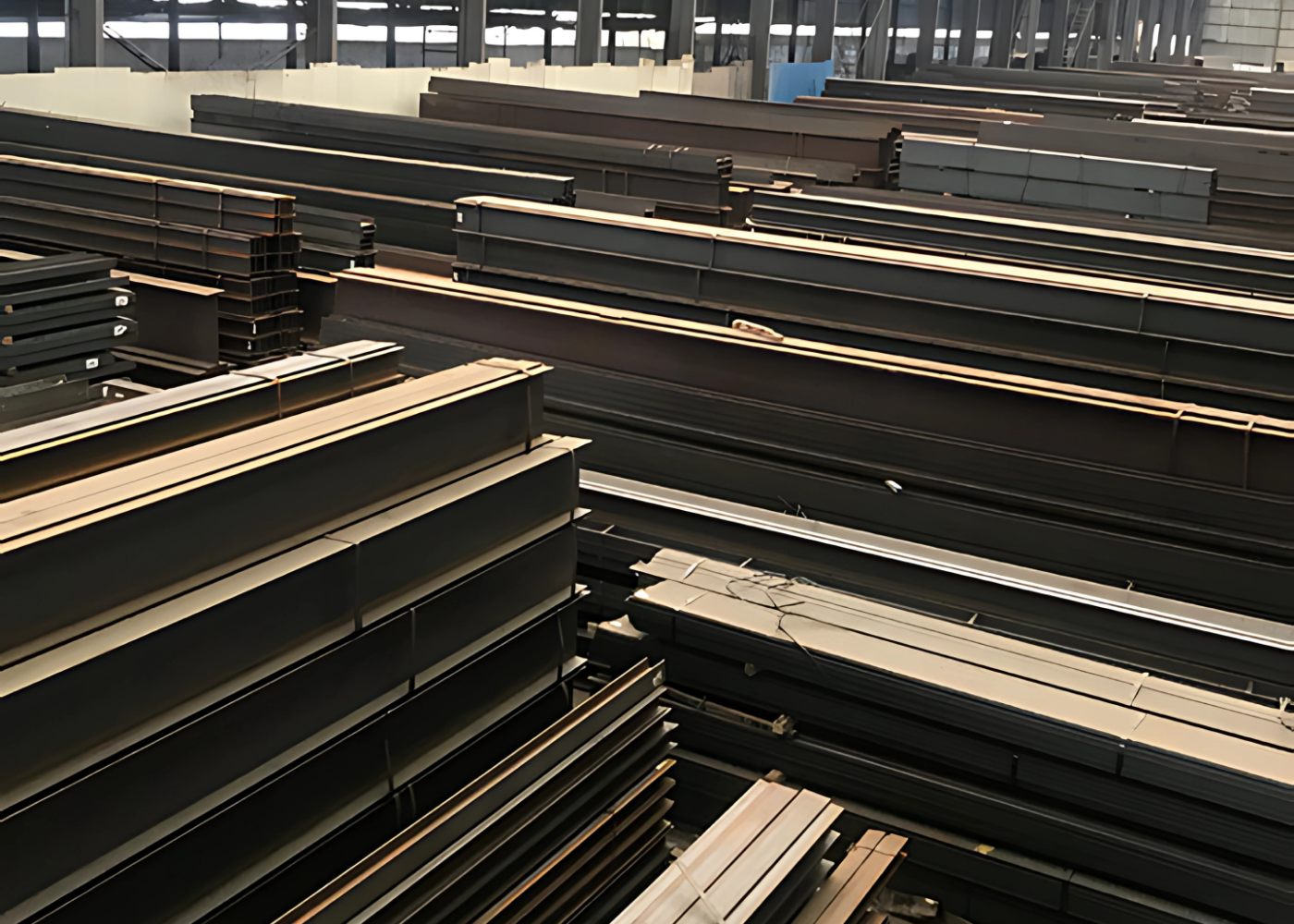
Introduction: What Are Hot Rolled H Piles?
H piles are hot-rolled steel sections with a characteristic “H” shape, designed for use in deep foundation applications. They are driven into the ground to transfer heavy vertical and lateral loads into deeper, more stable soil or rock layers.
Their slim web and wide flanges give H piles excellent penetration efficiency in dense soils and reliable load transfer capacity, making them a preferred choice for projects where other solutions may be less effective.
For engineers and contractors involved in infrastructure, marine works, and industrial construction, H piles remain a cornerstone of reliable foundation design.

Benefits of H Pile Beams in Deep Foundation Design
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: The distinctive narrow flanges of H piles enable them to penetrate dense soils with minimal resistance, reaching stable strata or bedrock effectively. This geometry ensures that vertical loads are transferred deep into the ground, making H piles a proven solution where high point bearing capacity is required.
- Versatility Across Applications: H piles are widely used across sectors—from supporting skyscraper foundations and bridge abutments to forming retaining walls, quay structures, and temporary cofferdams. Their adaptability to different soil conditions and project designs makes them a reliable choice for both permanent and temporary works.
- Standardised Design and Availability: Typically manufactured as hot-rolled steel beams (as per EN 10025 and EN 10248) with precise dimensions, produced in a wide range of sizes, with predictable section properties for engineering design. This standardisation guarantees predictable performance, simplifies engineering design, and reduces procurement lead times compared to non-standard alternatives.
- Excellent Driving Characteristics: H-pile shape has a slim web and narrow flanges, which reduce soil displacement and driving resistance, allowing for use in dense or rocky soil conditions. Steel piles can be driven with impact or vibratory hammers, depending on soil type.
- Reusability and Sustainability: In temporary works such as cofferdams or shoring systems, H piles can be extracted and redeployed. This reusability lowers lifecycle costs and supports sustainable construction practices by reducing material waste.
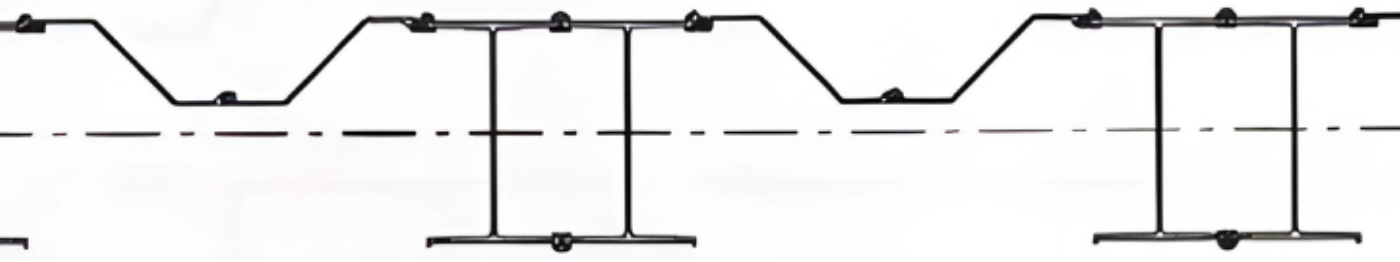
- Seamless Integration with Combi Walls: H piles are often used as king piles (bearing piles) in combi wall systems. Welded clutches or connectors enable seamless integration with sheet piles, resulting in walls with higher stiffness and bending resistance compared to regular sheet pile walls. This combination optimises both performance and cost-efficiency in marine structure applications and waterfront construction.
- Durability in Demanding Environments: Produced in grades such as S275, S355, and S430, and can be coated or galvanised to resist long-term corrosion in marine and industrial environments. When surfaces are protected with anti-corrosion coatings or galvanisation, H piles deliver reliable performance even in aggressive environments like tidal or splash zones. Additional design allowances for corrosion at mudline interfaces further extend their service life, ensuring structural integrity under harsh marine and industrial conditions.

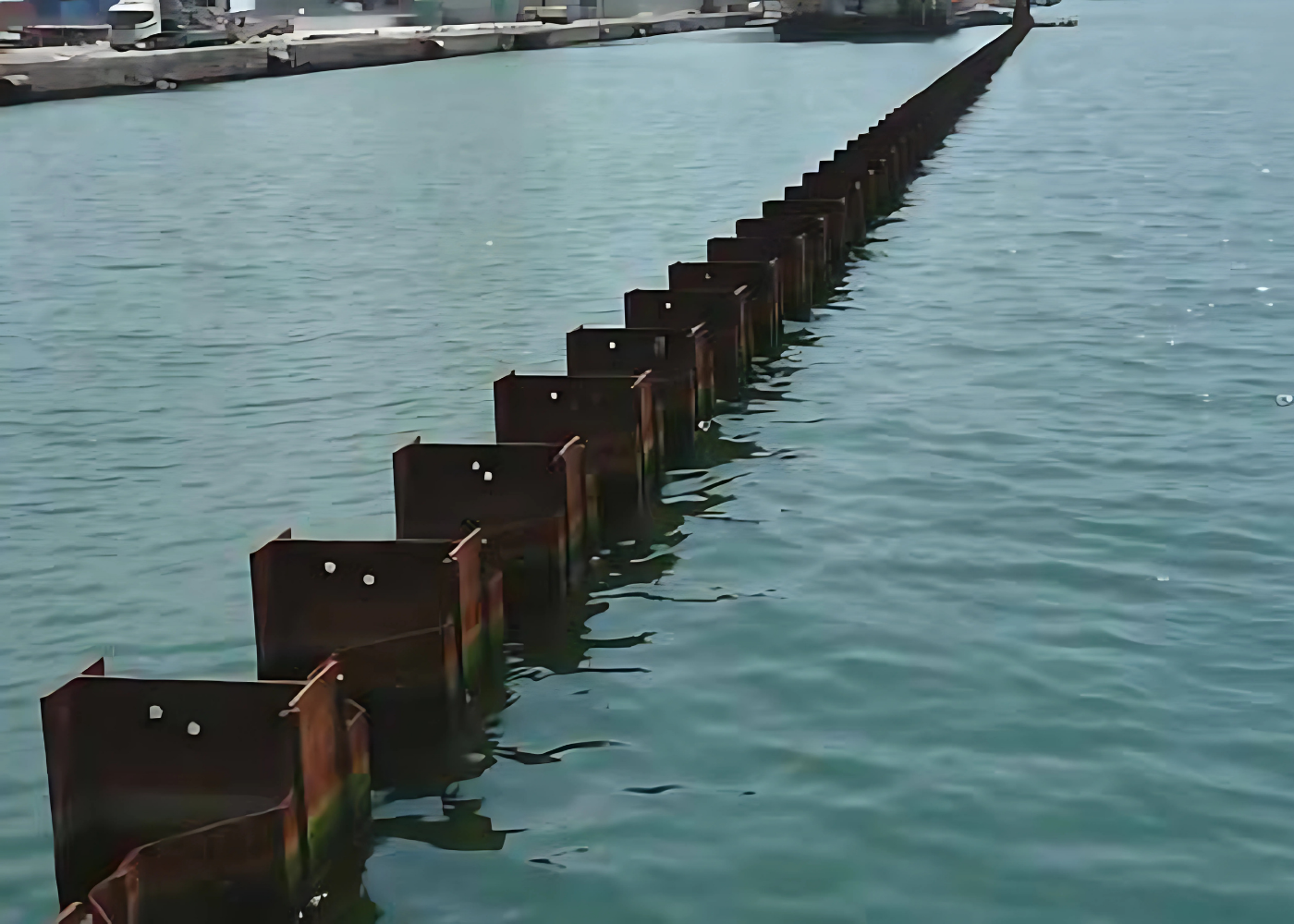
Applications of H Piles
Because of their geometry, strength, and drivability, H piles are among the most versatile deep foundation elements. They are specified across civil, marine, and industrial projects where reliable load transfer and durability are essential.
Civil Infrastructure
- High-Rise Buildings: Structural beams provide point bearing capacity to transfer heavy structural loads into stable strata.
- Bridges and Highways: Used for pile-supported abutments, piers, and approach structures where both axial and lateral resistance are required.
- Industrial Foundations: Support for refineries, power plants, and heavy machinery bases.
Marine and Waterfront Structures
- Ports & Harbours: Commonly used in quay walls, jetties, dolphins, and berths, either as independent piles or as king piles in combined wall systems.
- Flood Protection: Applied in levees, dikes, and seawalls to resist hydrostatic pressures and wave forces.
- Cofferdams: Temporary watertight enclosures built using H piles for excavation or underwater construction.
Temporary Works and Reusable Structures
- Shoring Systems: Support deep excavations in urban construction.
- Temporary Cofferdams and Retaining Walls: Can be extracted after use and redeployed in other projects, reducing overall material consumption.
Installation and Driving Methods
The performance of H piles depends not only on their section properties but also on how they are installed. Their slim profile and narrow flanges make them well-suited for driving into dense soils with minimal displacement. Still, proper equipment and methods are essential for achieving design depth and maintaining structural integrity.
Common Driving Techniques
- Impact Hammers: Deliver high-energy blows, ensuring penetration into dense soils or through obstructions.
- Vibratory Hammers: Quicker installation in granular soils, with reduced noise and vibration compared to impact methods.
- Press-in Systems: Hydraulic jacking methods are used in urban or environmentally sensitive areas where noise and vibration must be minimised.
Driving Aids
- Pre-Drilling: Used in very dense soils or mixed ground to ease pile penetration.
- Water Jetting: Can assist penetration in sandy or compact layers.
- Toe Reinforcement: Welding a driving shoe or reinforcing plate at the pile toe protects against damage in hard strata.
Practical Considerations
- Verticality and Alignment: Accurate positioning ensures load transfer and reduces bending stresses.
- Splicing: When greater depths are required, piles can be extended with welded or bolted splices.
- Soil Conditions: Driving resistance and vibration must be evaluated to prevent settlement impacts on adjacent structures.
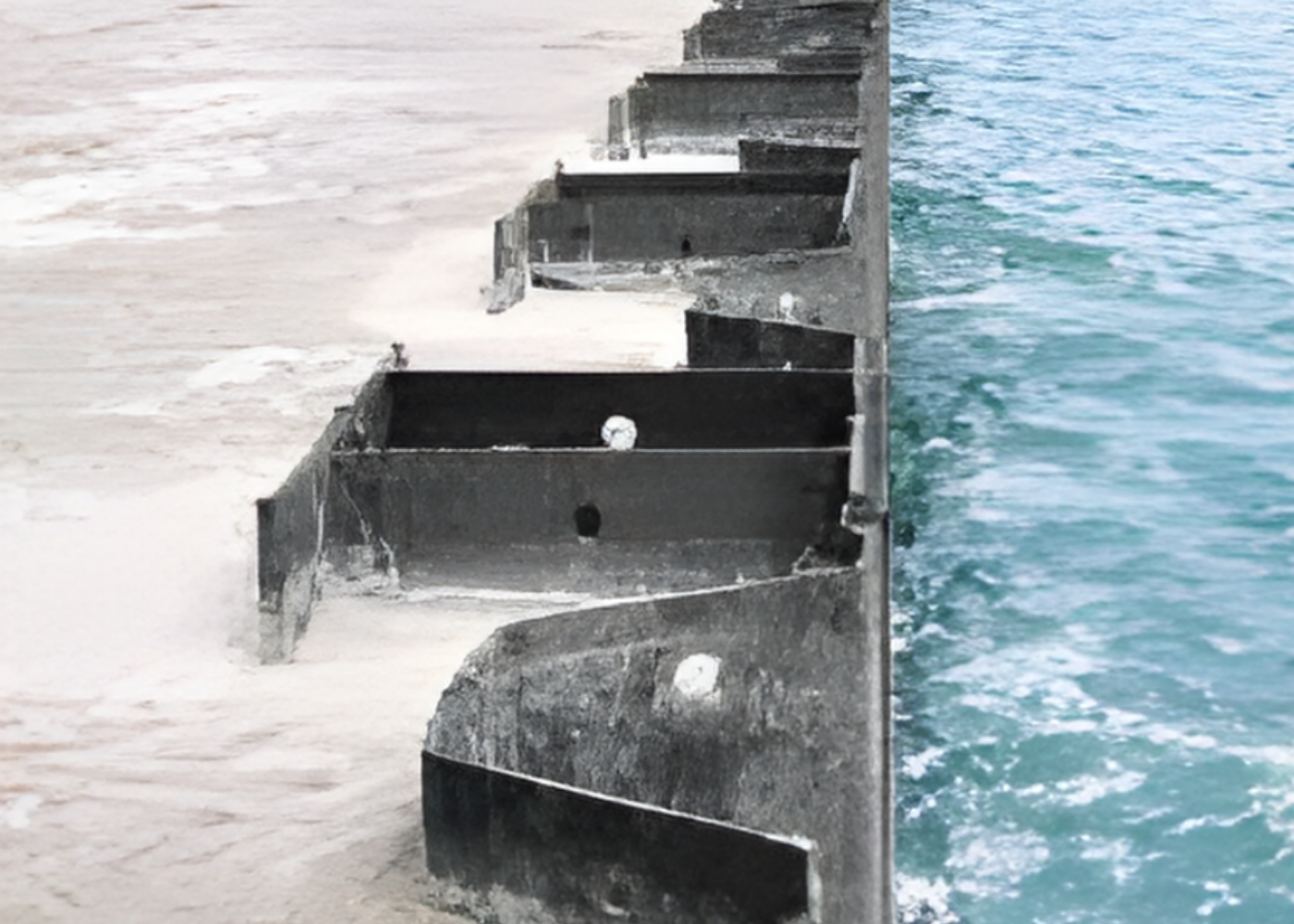

Durability and Corrosion Protection
H piles are frequently installed in harsh environments, including marine, tidal, and industrial zones, where corrosion is a critical design factor. Long-term performance depends on selecting the right steel grade and applying appropriate protection systems.
Protective measures for H piles typically include multi-layer coating systems, hot-dip galvanisation, and, where required, additional steel thickness at critical zones such as the mudline or splash areas. These strategies ensure long-term durability by reducing corrosion risk and maintaining the structural integrity of the foundation throughout its service life.
Structural Steel Grades: H piles are manufactured in structural grades with high mechanical strength, commonly from S355 and S430. These grades provide the balance of toughness, weldability, and load-bearing performance needed for demanding foundation works.
Service Life Considerations: With appropriate material selection and corrosion protection, H piles can remain in service for decades, even in aggressive marine or industrial environments. Service life expectations are always project-specific, balancing protection costs, maintenance requirements, and the intended design life of the structure.
Design Notes for Engineers
The performance of H piles is defined by their section properties, particularly the section modulus and moment of inertia. These values determine how much bending and axial load a pile can safely resist once driven into the ground. Hot-rolled H piles offer predictable section properties due to standardisation, making them straightforward to specify in structural calculations. For non-standard requirements, welded H piles can be designed with customised flange widths and web thicknesses to achieve the required stiffness and capacity.
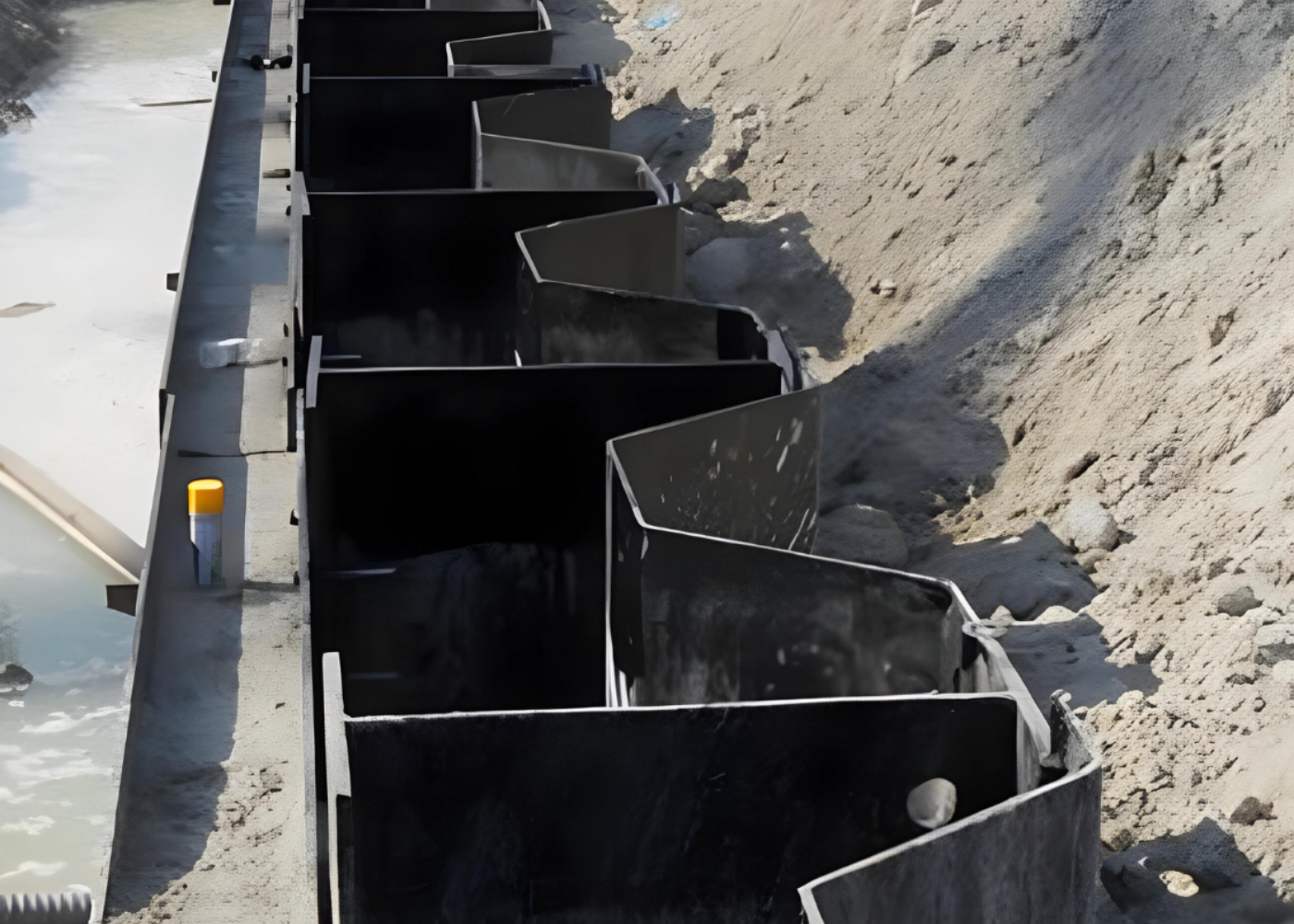

Practical Example
In many port expansion projects, H piles are specified as king piles in combi wall systems. By spacing them at intervals of approximately 2.0–3.5 m, engineers can achieve the required wall stiffness while using lighter sheet piles in between. This not only reduces overall steel tonnage but also speeds up installation, since fewer primary elements need to be driven. When protected against corrosion, such systems can provide reliable service for decades under heavy berthing forces, wave action, and tidal loads.
Conclusion
H piles continue to be one of the most reliable and widely used solutions in deep foundation engineering. Their combination of high load-bearing capacity, efficient drivability, and adaptability makes them indispensable for civil, marine, and industrial projects.
While alternative piling systems may be chosen for specific ground conditions, Hot-rolled H piles continue to be the go-to choice for foundation systems that require strength, economy, and availability. For projects requiring special dimensions or enhanced section properties, welded H piles can be used as a flexible alternative that can be tailored to exact design needs.
Whether used independently or as part of a combi wall system, H piles offer the strength, durability, and proven performance that engineers and contractors trust to build lasting infrastructure.
Related Products from Aema Steel
- Welded H Piles
- Steel Tie Rod Systems
- Hot Rolled U Type Sheet Piles
- Hot Rolled Z Type Sheet Piles
- Steel Pipe Piles
Contact us today to receive a tailored offer for your upcoming project.