Guide Overview:
-
Types of Sheet Pile Sealant;
-
Key Considerations for Sheet Pile Sealing;
-
Factors Affecting Water-tightness;
-
Common Mistakes to Avoid;
-
Applications and Benefits of Sheet Pile Sealing;
-
Installation and Maintenance;
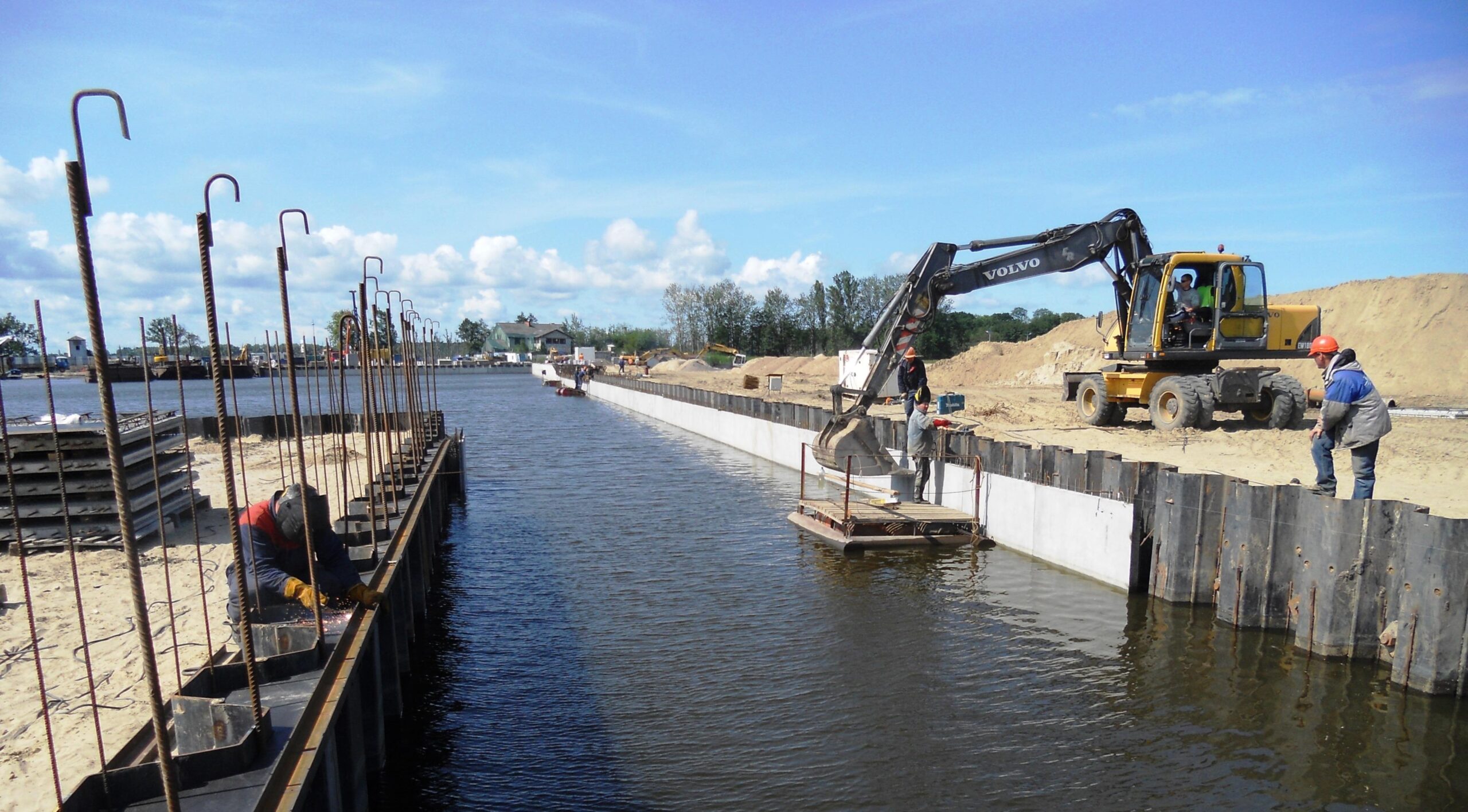
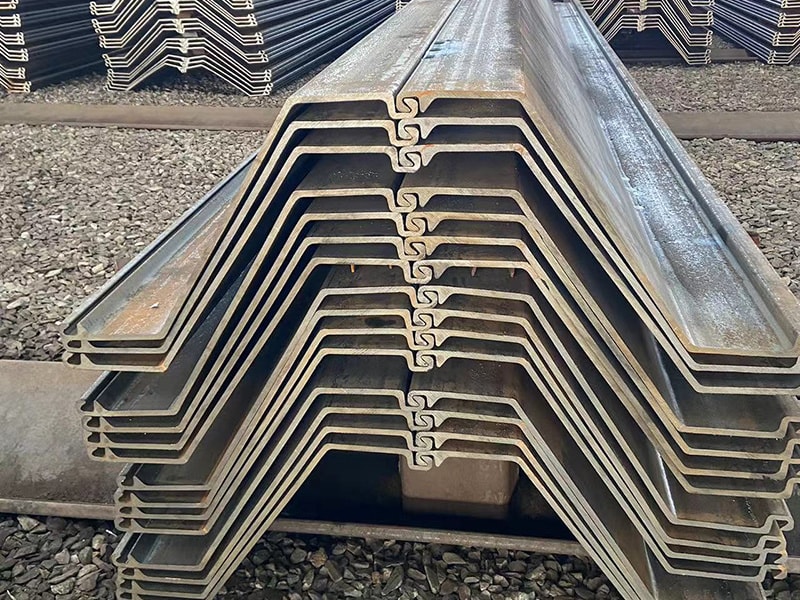
For projects where groundwater control is crucial—basements, underground parking, reinforced concrete capping beams, containment barriers, bridge abutments, temporary retaining walls and cofferdams—sheet pile water tightness is key. Small gaps between sheet pile interlocks (clutches) facilitate installation but allow water seepage. To make a reliable barrier (sheet pile wall) and make sheet pile systems watertight, these gaps are sealed with specific interlock sealants, a solution to keep the foundation dry, stable and secure.
Types of Sheet Pile Sealant
Natural Sealant
Natural sealing occurs when soil, sand, or other natural materials fill the sheet pile interlock gaps, creating a cost-effective solution against water seepage. This approach is environmentally friendly and effective, especially in areas with low water pressure or stable site conditions. However, natural sealing often requires additional support for high water pressure, difficult soil, or areas with tropical or arctic conditions, as extreme temperatures can degrade natural seals.
Artificial Sealant
Artificial sealing uses engineered materials to create a controlled, durable seal within sheet pile clutches gaps. This is more reliable in challenging ground and weather conditions. There are several types of artificial sealants:
Asphalt Mixtures: Asphalt mixed with fillers such as sawdust can be applied to the sheet pile interlock gaps, creating a flexible and durable seal. These sealing systems work well in moderate conditions but may need reapplication in areas exposed to aggressive water environments and weather conditions over time.
Example: Asphalt sealing is often used in city flood control and site remediation projects because it is durable and easy to maintain.
Water-Swelling Materials (WSM): WSMs are designed to expand on contact with water (liquid), forming a flexible, self-healing seal with a high expansion coefficient perfect for fluctuating conditions. This sealant is often used in tunnels, underwater, and high-pressure applications, as it can fill irregular surfaces and form a reliable barrier. However, WSMs require precise handling to avoid overexpansion, which can stress the steel sheet pile interlocks.
Example: WSMs are commonly used in riverbank stabilisation projects because they adapt well to natural water level changes.
Advanced Sealants: These are specialised resins, such as polyurethane, that cure and expand when in contact with water, creating a highly durable and resilient seal. They are more expensive but ideal for projects that require extreme water resistance and long-term durability. Polyurethane sealants are used in coastal defence since they help structures withstand constant exposure to seawater.
Magnetic Sealants: Magnetic rubber strips with magnets embedded are prefabricated and can be placed into interlock gaps, creating an effective watertight seal under varying water pressure. Magnetic sealants are quick to install, but periodic inspections are required for long-term effectiveness.
Example: Magnetic sealants are often used in temporary cofferdams, as they are easy to remove after construction.
Welded Interlocks: Welding steel sheet pile interlocks are the permanent solution for projects where water tightness is critical, such as basements or high-risk containment barriers. More preparation is required, but seal welding is ideal when total water control is needed. Double piles with a seal-welded intermediate interlock are recommended for high seepage resistance.
Example: Welded interlocks are widely used in high-rise basement construction, creating a waterproof barrier where eliminating any water leakage is critical.

Key Considerations for Steel Sheet Pile Walls Sealing
Watertight sealing goes beyond just filling gaps; it means addressing all connection points where steel sheet piles meet other structural elements. Ground conditions, groundwater level, environmental exposure and pile alignment are key to achieving long-lasting seals.
Connection Points: The sealant must accommodate complex junctions where sheet piles meet anchors or ring strips. These connection points are under extra stress, so a high-performing joint sealant is required. Proper joint preparation ensures that round bars or welded reinforcements maintain high adhesive strength.
Joint Preparation: Proper joint preparation is critical for sealing. Clean the sheet pile interlock surface thoroughly to remove any mill scale, rust or previous sealant. Cleaning improves adhesion and extends the lifespan, reducing the risk of corrosion inside. Achieving clean and free interlocks during the preparation stage improves the sealant application.
Environmental Conditions: Temperature and humidity during application can affect the sealant’s performance. High humidity will slow down curing, and extreme temperatures can affect the flexibility and reliability of some sealants. Selecting the right sheet pile sealant for site conditions ensures optimal results. Not all sealants are environmentally friendly and non-toxic. Look at the technical information and specifications of the sealant product before use.
Watertightness Factors
Several factors can affect water tightness in sheet piling projects. Water can only get through a sheet pile wall through the interlock. Sealants can reduce leakage through sheet pile walls by 95%, significantly improving the sealing quality and almost making sheet piles watertight.
Understanding and addressing these factors will improve the reliability of your sealing:
Condition of the Steel Sheet Piles:
Rust, warping, or deformations in the steel sheet piles can compromise the interlock joints’ seal and tight fit.
Example: A routine visual inspection before sheet pile installation can identify any deformations that could impact the watertight seal, ensuring each sheet pile is in the best condition.
Installation Quality:
Proper sheet pile driving is key. Precision in fitting each pile and double-checking alignment will maintain a continuous seal. Advanced installation equipment such as silent pressing machines or telescopic leader rigs can improve alignment, especially in difficult soil conditions.
Construction Environment:
Site conditions, including water pressure, installation depth, soil stability, and ground water quality, will determine the suitable sealing method and the degree of watertightness.
Example: Typically, high water-pressure environments require compression or water-swelling sealants, while areas with unstable soil may require additional structural reinforcement.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with suitable materials and methods, installation mistakes can compromise water tightness. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Poor Joint Preparation: Applying sealant to dirty or rusty surfaces will prevent the sealant from adhering correctly and create potential weak points. Cleaning before application is critical for a strong seal.
Wrong Sealant Choice: Not all sealants are suitable for every environment, so using water-swelling material in a non-humid environment, for example, will reduce its performance. Ensure the sealant matches soil and water conditions for the best performance.
Misaligned Piles in Sheet Pile Wall: Interlock gaps or inconsistencies allow water to seep if piles are not aligned properly. Ensure each pile is aligned with the previous one and check fit during installation.
Incorrect Sealant Application: Applying sealant unevenly, too thinly, or too thickly will reduce its performance. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for consistent coverage and maximum sealing power.
By avoiding these mistakes, you will save time, reduce costs and get a reliable seal for your project.
Additional Applications and Sustainable Benefits of Sheet Pile Sealing
Basement and Substructure Use
Steel sheet piles are increasingly used in basement construction as advanced sealing options now allow for watertight walls without on-site welding. Using wider piles and high-performance sealants has made steel substructures more attractive for various basement grades, from moisture-tolerant storage spaces to dry, conditioned environments.
Containment Barriers
Sealed sheet pile walls are effective in containment applications, preventing contaminants from leaching into groundwater. Compared to traditional methods like clay bunds, sealed sheet pile barriers take up less footprint and can be installed at site boundaries, maximising usable ground space. This makes them perfect for site remediation, redeveloped sites with contamination issues, and environmental conservation efforts.
Sustainable Design and Demountable Foundations
In a world of flexible building use, steel sheet piles offer sustainability benefits by being removable, reusable or recyclable. By designing with demountable foundations, construction projects will minimise site obstructions and future redevelopment and create sustainable products and sites.
Example: In urban redevelopment, sheet piles used in temporary structures can be reused in new projects, reducing the need for additional resources and promoting a circular economy.
Installation and Maintenance
Both workshop and on-site application techniques require attention to achieve long-term performance. Preparing interlocks before applying sealant in a controlled environment will give the best results and minimise exposure to weather, debris, or moisture.
Automated machines can apply hot-applied bitumen sealant to steel sheet pile interlocks, reducing manual handling risks and improving application accuracy. This automation minimises the risk of spills and burns from hot sealants, making the process safer and more efficient. Manual application of hot-applied joint sealant can pose health risks, such as burns from splashing and respiratory issues from fumes. Workers need training to make sealants safe and practical application in piling projects, especially for cut-off walls and high-resistance applications.
During installation, pitch-and-drive can improve sealant integrity, and pitch-and-drive methods reduce sealant disturbance. For permanent installations like basements, sealing interlocks post-installation with a fillet weld or using a protective layer for hydrophilic sealants will keep the structure watertight.
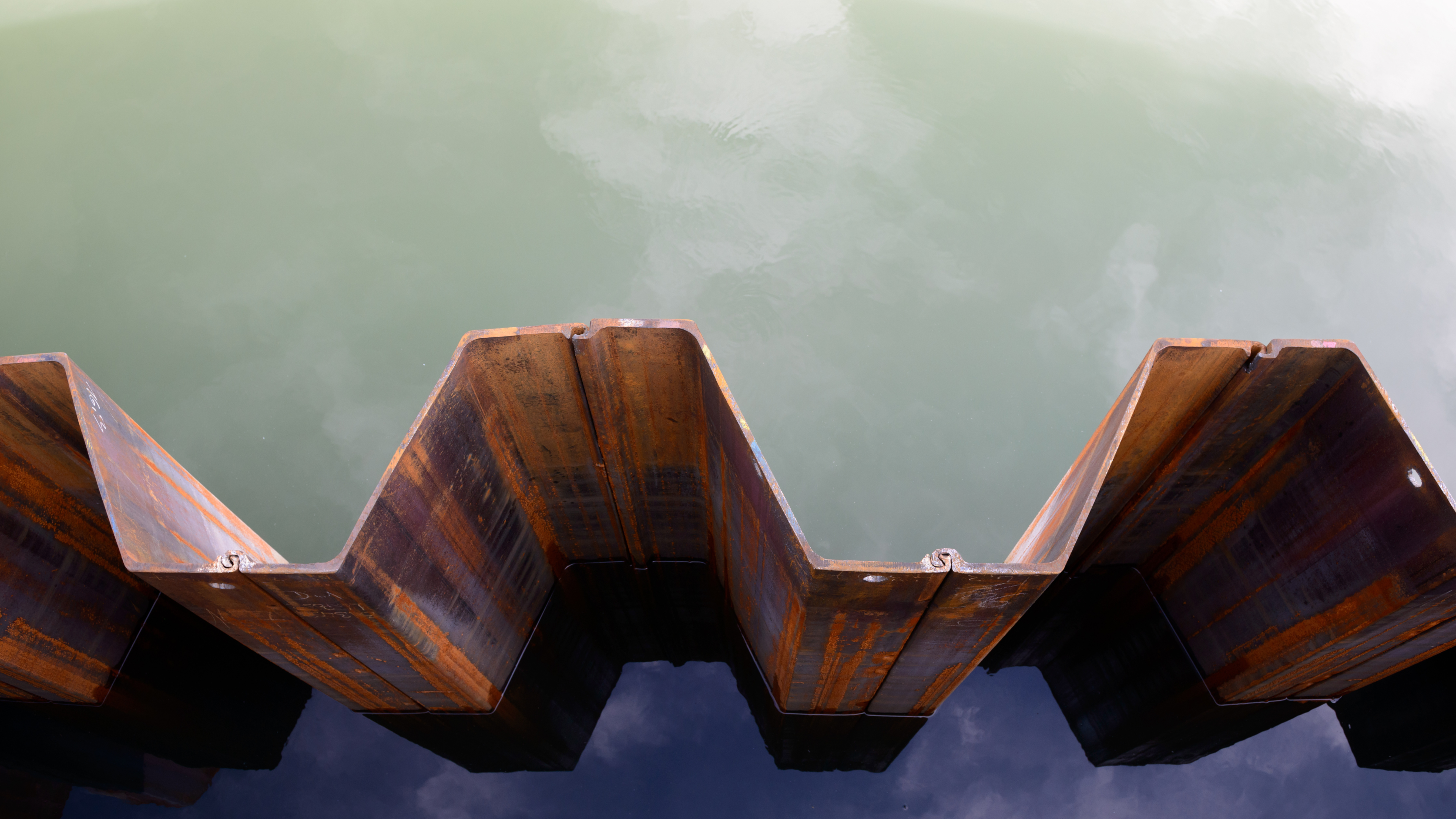
Conclusion
Choosing the right sealant system, considering the environment, and avoiding common installation mistakes will make all the difference in getting a practical and durable watertight seal and preventing water leakage for your steel sheet piling project. By following these practices, preparing well, and adhering to sealing guidelines, your foundation will be dry, stable like concrete, and resilient for years to come.
Related Products from Aema Steel
- Hot Rolled U Type Sheet Piles
- Hot Rolled Z Type Sheet Piles
- Cold Formed U Type Sheet Piles
- Cold Formed Z Type Sheet Piles
- Steel Pipe Piles
- Welded H Piles
Contact us today to receive a tailored offer for your upcoming project.